It’s helpful to distinguish between VPNs for personal use and those used in a professional context. Although they share similar core technology, a business VPN is designed to meet specific security challenges, access management, and data protection in a professional environment. These fundamental differences in usage and objectives between personal and business VPNs warrant a detailed exploration to understand their respective values in our connected world.
What is a VPN?
A VPN is a service that creates a secure tunnel over the internet. By encrypting data exchanged between your computer and the VPN servers, it ensures your information (in this case, business-related) remains private and safe from prying eyes.
A VPN operates by establishing a secure and encrypted connection between your device and a remote server, managed by the VPN service provider (or a business telecom operator). In the consumer context (as opposed to Business VPN), this encryption process prevents anyone from monitoring or intercepting your online activities. By hiding your real IP address, a VPN also allows you to bypass censorship or geographical restrictions.
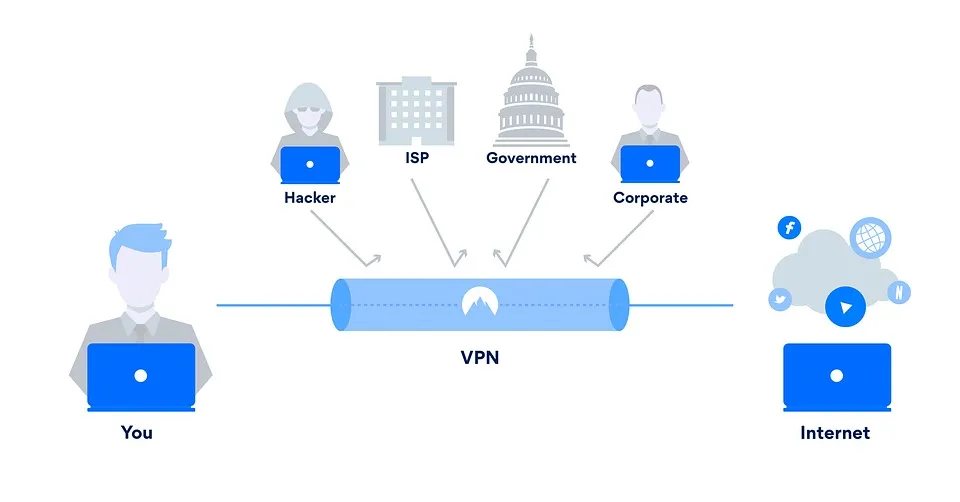
How Does the Business VPN Operate?
The operation of a business VPN is structured around three key components:
- A dedicated VPN server
- VPN softwares on endpoints (smartphone, tablet, computer)
- Robust security protocols.
The VPN server acts as a secure intermediary between remote employees and the company’s IT resources. This infrastructure enables employees to work remotely with the same level of security and access to resources as they would have in the office, thus ensuring business operations continuity and the protection of the company’s sensitive data.
To access the company’s network, employees use VPN apps installed on their workstations or smartphones. These applications establish a secure and encrypted connection with the VPN server, ensuring all transmitted data remains private and protected.
Integrating the VPN into the Company’s Information System
Integrating a business VPN begins with setting up a robust VPN server, either within the company’s infrastructure or hosted in the cloud. This requires careful configuration to ensure the server is secure, accessible, and capable of handling the expected volume of traffic. Next, VPN applications are deployed on employees’ devices. These applications are specifically designed to connect securely to the company’s network, offering an easy-to-use interface to initiate and manage the VPN connection.
Security Protocols
Security protocols, such as IPSec, L2TP, or OpenVPN (a free and open-source software), play a crucial role in securing the connection between employees’ devices and the VPN server. These protocols ensure data is encrypted before leaving the employee’s device, guaranteeing that information remains secure throughout its journey over the public internet to the company’s VPN server.
Remote Work : why use a VPN ?
With the rise of remote work, business VPNs have become an indispensable tool for ensuring security and efficiency in working from afar. The VPN provides employees, collaborators, and certified consultants with secure access to the company’s internal resources and systems. Regardless of their location, VPNs facilitate collaboration and productivity while protecting against data leaks and targeted cyberattacks.
How Does It Differ from a VPN for Personal Use?
While the basic principle remains the same, business VPNs offer features and security levels tailored to the specific needs of organisations.
- VPNs for the general public mainly focus on privacy protection and bypassing geo-restrictions.
- Business VPNs are designed to secure company communications and sensitive data, facilitate remote access management, and ensure broad compatibility with existing IT infrastructure.
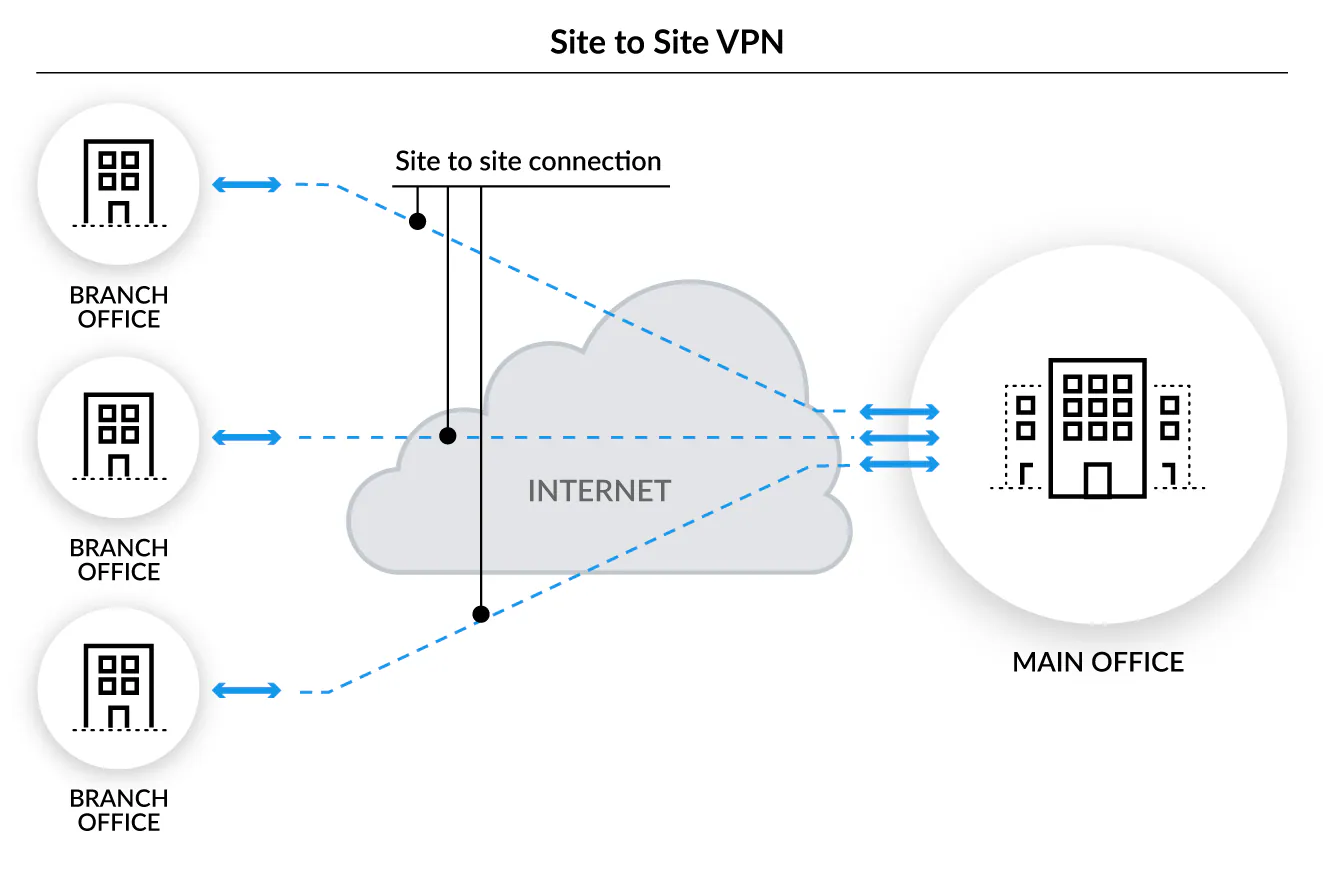
Company Across Multiple Locations or Sites : The Role of VPN
As previously discussed in the context of Layer 2 connectivity with optical fibre, VPNs can link multiple sites of the same company, thus creating a secure and extended corporate network.
This use of a VPN is often referred to as a VPN tunnel or a Site-to-Site VPN. This type of VPN is designed to securely connect the networks of various physical locations of a company, as if these different sites were connected by a long virtual cable.
- Each site has a VPN device that manages the connection to the rest of the company network. Data travelling between sites is encrypted, ensuring the security and privacy of the exchanged information.
- Employees from different sites can access the same network resources and applications
- For whom? Site-to-Site VPNs are particularly useful for companies with offices spread across multiple geographical areas, allowing them to maintain consistent and secure network connectivity without the costs and complexity associated with direct physical connection solutions, such as leased lines.
Upload Speed and VPN: Understanding and Choosing Wisely
The use of a business VPN requires a robust internet connection and a telecom carrier dedicated to businesses. This is where professional internet connections truly stand out compared to home internet services intended for individuals and families, especially in terms of upload speed.
Example: A company with gigabit coaxial cable connectivity will suffer from limited upload speeds of 20 or 50 Mbps, whereas optical fibre, for example, offers symmetric speeds of 500/500 Mbps, 1/1 Gbps. Result: smooth and efficient communication between remote employees and the company’s servers.
A slow connection or insufficient upload speed will compromise the benefits of remote work. Investing in a quality internet connection is thus essential to maximise the benefits of a business VPN, whether for a SME (small or medium-sized company) or a large enterprise.




